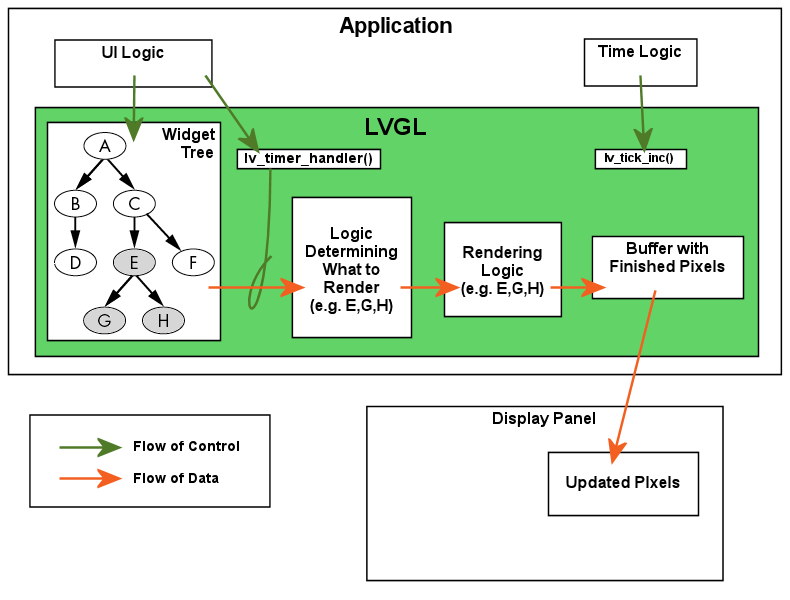
Timer Handler
To drive the timers of LVGL you need to call lv_timer_handler()
periodically in one of the following:
while(1) of main() function, or
an OS task periodically. (See LVGL and Threads.)
Example:
while(1) {
uint32_t time_till_next = lv_timer_handler();
my_delay_ms(time_till_next);
}
If you want to use lv_timer_handler() in a super-loop, a helper
function lv_timer_handler_run_in_period() is provided to simplify
supplying LVGL with time awareness:
while(1) {
...
lv_timer_handler_run_in_period(5); /* run lv_timer_handler() every 5ms */
...
}
Or use the sleep time automatically calculated by LVGL:
while(1) {
...
lv_timer_periodic_handler();
...
}
In an OS environment, you can use it together with the delay or sleep provided by OS to release CPU whenever possible:
while (1) {
uint32_t time_till_next = lv_timer_handler();
os_delay_ms(time_till_next); /* delay to avoid unnecessary polling */
}
See Timer (lv_timer) section to learn more about timers.